1. What is meant by 'Degrees of freedom'?
Ensure you include a diagram to highlight your understanding. (p. 253)
Robots are designed to carry out movement. The amount of movement is –determined by the degrees of freedom built into the design. Degrees of freedom are the number of different ways an attachment can pivot. A human has seven degrees of freedom as it is able to rotate in seven different ways.
Robots are designed to carry out movement. The amount of movement is –determined by the degrees of freedom built into the design. Degrees of freedom are the number of different ways an attachment can pivot. A human has seven degrees of freedom as it is able to rotate in seven different ways.
NOTE: No robot, or computer program will
function unless it has some form of input and/or output to display the
processed data.There are many ways of inputting and outputting data into a
robotic system
2. There are 5 general input devices used
in robotics. List them below. (p. 254)
1. Digital Camera
2. Keyboard
3. Light Pen
4. Mouse
5. Microphone
2. Keyboard
3. Light Pen
4. Mouse
5. Microphone
3. Sensors are a common input device on
robotics. Complete the following table (see p. 254 to 255)
Sensor Name
|
Description
|
Examples of use
|
Potential Issues
|
Thermostat
|
Switch that opens at
a set temperature and stays open while the temperature remains at the level
or higher.
|
Ovens,
hot-water system
|
Not as accurate or
as quick to respond as other sensors but they are cheap.
|
Thermistor
|
Measures temperature
continually as resistance: when the temperature increases, resistance drops
|
Microwave ovens, air
conditioners
|
Similar to
thermostat and also cheap.
|
Semiconductor
|
Are sensor materials
with electrical properties that are not as good as those of good electrical
conductors such as copper wire but not as poor as non-electrical conductors.
|
Silicon base
|
Not great conductors, but not poor either
|
Light
|
Light sensors detect
changes in the level of light.
|
Driveway lights
|
Not very
durable
|
Position
|
A position sensor
would be a simple contact sensor a switch that could be ether turned on or
off
|
Light switch
|
Can be unreliable
|
Potentiometers
|
Used to determine
rotation. They work on electrical resistance and the meter shows the amount
of voltage at a particular point.
|
Used in robotics
|
Only gives a fairly
accurate reading - not as accurate as other types of sensors
|
Sonar
|
Uses sound
to determine position of objects, by bouncing sound waves off objects.
|
Submarines use sonar
to see other boats on the water.
|
Not as accurate as
other types of sensors
|
4. Define and compare an Actuator to a
Sensor
Actuator: An actuator does the work of a
system but doesn't actually obtain that information
Sensor: A sensor collects data from the
environment through the use of sensor mediums.
Sensors take the information from and
environment so that the actuators carry out action using the information
provided.
5. Actuators are a common output device on
robotics. Complete the following table (see p. 256)
.
Output devices
|
Description and main feature
|
Advantage
|
Disadvantage
|
Speakers
|
Speakers volume control; available to a wide range
of people.
|
Normal speech rather than synthesised speech is
available
|
Requires extra hardware like a sound card
|
Display (CRT or LCD)
|
Available for many applications
|
no waste of paper; can be interactive
|
No hard copy
|
Solenoids
(an actuator)
|
Use an electromagnet to move an arm or plunger
through a small movement.
|
Easily pushes and pulls and objects
|
Requires extra hardware for
operation. Electric currents may prove to be harmful.
|
Stepping motors
(an actuator)
|
Uses electromagnets to measure rotations of a motor
around the spindle to measure its position.
|
Gives good accurate measurements of the rotations of
wheels etc..
|
Not durable and can often contribute to noise
pollution
|
Position
|
Can be a simple contact sensor like a switch or can
be more complex in which it could calculate how far an object is from it.
|
Offers optimal performance for operating arms and
their degrees of movement
|
Can very buggy and takes a while to program it for
optimal performance
|
Potentiometers
|
Used to determine rotation by harnessing electrical
resistance and shows the voltage at a certain point
|
Very good at measuring rotations to a high standard
|
Not as accurate readings as other sensors but still
quite good
|
Sonar
|
Uses sound to determine position by using high
frequencies which bounce off objects
|
Can be used to locate objects from great distances
|
Changes in the environment, such as
temperature, pressure, humidity, air turbulence and airborne particles affect
response.
|
6. Define Primary Storage and provides
examples (p. 257)
Primary storage,
which is found on the motherboard and holds data for processing, processed data waiting to be outputted and
instructions for processing. It also acts as a link between computers and their
secondary permanent storage. Primary storage is needed so that tasks/
instructions can be carried out efficiently. Can be either permanent, ROM, or
temporary, RAM. A computer cache is an example of primary storage.
7. Define Secondary Storage and provide
examples
Secondary storage is anything that is not part of the
CPU. The size of your secondary storage is determines the ability of the system
to store information for future use. An example of secondary
storage would be a hard drive or DVD.
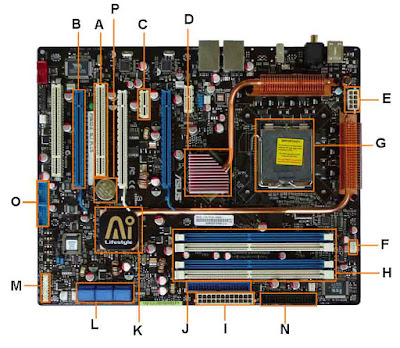
8. Using the following diagram, write below
what each letter represents. You will find an overview of this motherboard at
http://www.build-your-own-computer.net/motherboard-diagram.html
A:PCI Slot
B:PCI-E 16x Slot
C:PCI-E 1x Slot
D:Northbridge
E:ATX 12V 2X and 4
Pin Power Connection
F:CPU-Fan
G:Socket
H:Memory Slots
I:ATX Power Connector
J:IDE Connection
K:Southbridge
L:SATA Connections
M:Front Panel Connections
N:FDD Connection
O:External USB
Connections
P:CMOS battery

No comments:
Post a Comment